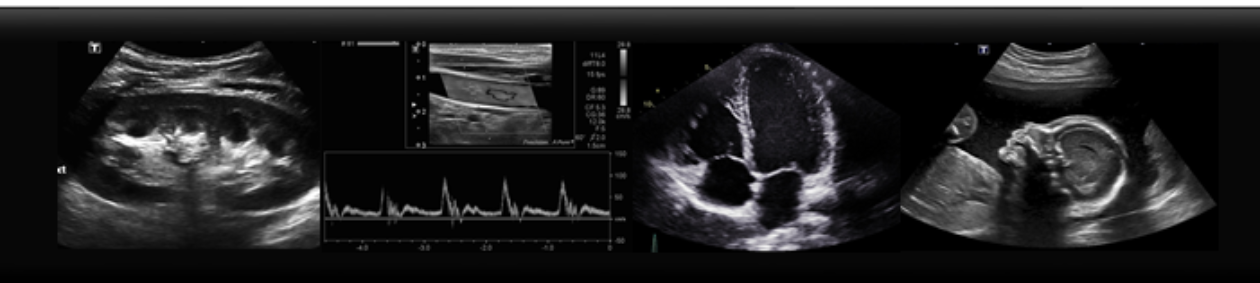
Cholecystitis is one of the more common ailments seen in emergency departments, and one of the most frequent indications for an abdominal ultrasound. Gallstones will appear as echogenic, or bright white, round stones within the gallbladder, with shadows posterior. The gallbladder itself will appear anechoic, or black, tubular structure, adjacent to the right lobe of the liver and the main portal vein. When assessing for cholecystitis here are some other sonographic signs:


-Look for mobility. Do the stones roll when you move the patient? Look at the gallbladder supine, stone will be sitting towards the “neck” of the gallbladder, because that is dependent location. Now try tolling your patient LLD, or even sitting up. The stones should roll to the fundus! If not, are they stuck in the neck?

– Is the gallbladder wall thick? Measure the wall in transverse and it should be less than 3 mm

-Is there free fluid? Look for a pointy, “triangle” shaped anechoic area beside the GB.

– Is there a positive Murphy’s Sign? When you apply pressure to the gallbladder, does this correspond with the patient’s area of pain? Often the response is quite clear.
Images courtesy of Radiopedia.org:
Case courtesy of Dr Derek Smith, <a href=”https://radiopaedia.org/”>Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href=”https://radiopaedia.org/cases/42795″>rID: 42795</a>
Case courtesy of Dr Andrew Dixon, <a href=”https://radiopaedia.org/”>Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href=”https://radiopaedia.org/cases/9558″>rID: 9558</a>
Case courtesy of RMH Core Conditions, <a href=”https://radiopaedia.org/”>Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href=”https://radiopaedia.org/cases/38022″>rID: 38022</a>
Case courtesy of Dr M Osama Yonso, <a href=”https://radiopaedia.org/”>Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href=”https://radiopaedia.org/cases/16769″>rID: 16769</a>
Save
Save



![C60_Liver_IVC_Midline[3]_1](https://i0.wp.com/www.figbus.net/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/C60_Liver_IVC_Midline3_1.jpg?resize=326%2C217)





